This guide covers the setup of AWS CodePipeline’s Source step which uses cross-account access. This Source step will poll for changes in a CodeCommit repository located within a separate account from the one that the CodePipeline is located in. Through the rest of this guide, Source account will represent the account that holds our CodeCommit repository, and the Destination account will represent the account that holds our CodePipeline and its resources.
Architecture

Source Account.
Other than our CodeCommit repository, we need to set up an IAM Role which will be assumed by our CodePipeline. First we have to set up the AssumeRolePolicy for our IAM role so that the Destination account can assume this role.

Following IAM Role policies must also be configured:
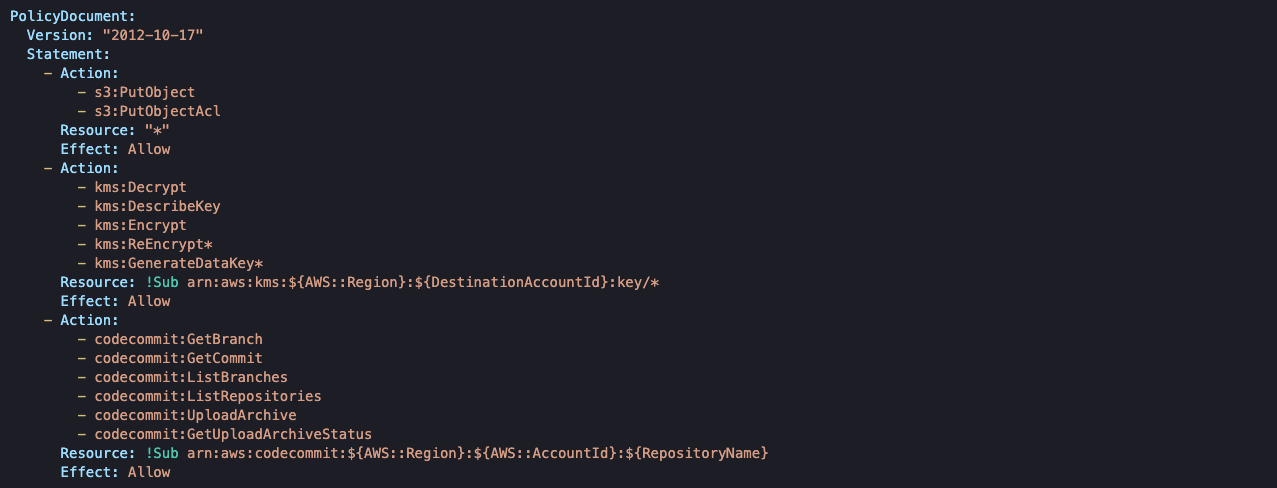
The policies defined above allow us to execute the following actions:
- Push repository artifacts into Destination account’s S3
- Encrypt the artifacts using Destination account’s KMS key
- Poll for changes in our CodeCommit repository
Destination Account
After we’ve set up our cross-account IAM Role in the Source account, we can create the rest of our resources in the Destination account.
KMS Key
When copying objects across two accounts, we have to use a Customer managed KMS Key in order to be able to both encrypt and decrypt those objects using Source account and Destination account roles.
To acomplish this, we will create a KMS Key and define a policy that allows usage of this key to both accounts:

S3 Bucket
We also need an S3 Bucket where we’ll store CodePipeline artifacts. In our case, an artifact is an archive, generated by the CodePipeline’s Source step, that holds CodeCommit repository contents.
To set up Bucket Encryption using the KMS Key we’ve previously created, we’ll add the following bucket property:

To allow cross-account access to the bucket, we’ll be setting up the following bucket policy:

CodePipeline IAM Role
Our CodePipeline needs an IAM Role with permissions which will allow it to assume the Source account role, fetch objects from the pipeline’s artifacts bucket, use the KMS key, write output logs into CloudWatch and finally invoke CodeBuild steps and output logs to CloudWatch.

CodePipeline
Now we’ll go through the pipeline itself. In order for it to work properly, we need to set up following properties:
- EncryptionKey – KMS encryption key we’ve created in the Destination account
- RoleArn (Source stage section) – IAM Role we’ve created in the Source Account
- RepositoryName – Source account’s CodeCommit repository name
- BranchName – Name of the Source account’s CodeCommit repository branch from which the pipeline will pull the contents

